Gum Disease
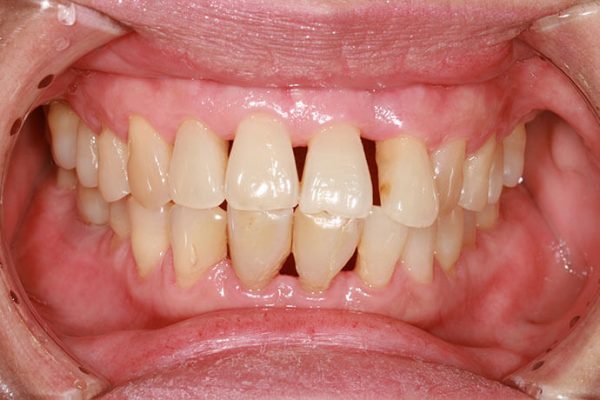
Gum disease or periodontal disease is an infection caused by bacteria that inhabit the oral cavity. It is the number one cause of adult tooth loss in the United States and 3 out of 4 adults may develop some form of gum disease. Periodontal disease is a silent infection that can affect your health as it is associated with systemic conditions such as atherosclerosis, myocardial infarctions, stroke, pneumonia, diabetes mellitus and low birth weight.
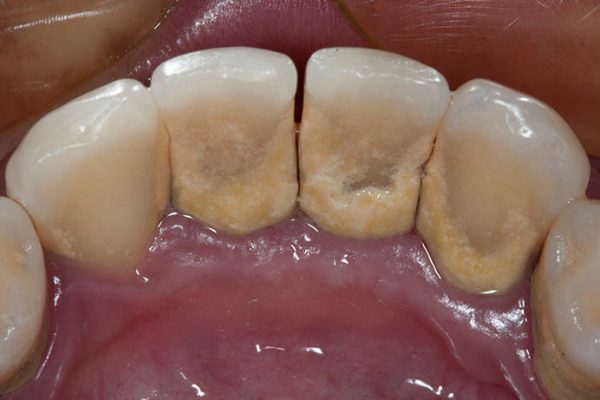
This disease begins as progressive gingivitis (inflammation of the gums). As the bacteria in the mouth proliferate and penetrate the space between the teeth and the gum tissue surrounding them, the body produces an immune response releasing chemicals that in time lead to bone loss around the roots of the affected teeth. This can create abscesses (swelling, infection), pain, bad breath, bleeding gums and eventual tooth loss. The bacterial agents that cause periodontitis evolve into great numbers due to an increased acidity in the oral environment; because of microscopic food particles that have not been eliminated.
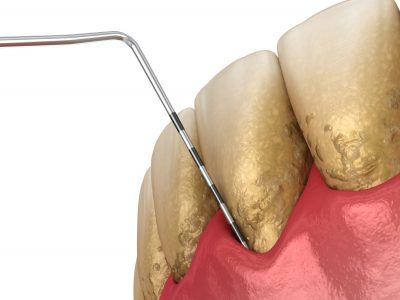
Periodontitis is diagnosed through the use of a periodontal probe which is an instrument that measures the gum surrounding each tooth. In conjunction with the dental probing numbers and X-rays, clinical data is collected to formulate a final treatment plan. The disease is treated and can be controlled through scaling and root planing, commonly referred to as deep cleaning. Localized and systemic antibiotic agents may also be recommended as adjunctive therapy to help expedite the gum’s healing process through the elimination of bacteria.